Efficient Hemoglobin Removal Advances Red Cell Proteomics Offering Many New Insights Into Inflammation and Infectious Disease
Background
Red Blood Cells (RBCs) are the subjects of extensive research, due to their functional relevance and associated disease states, such as sickle cell anemia, Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria, thalassaemia, malaria, and Parkinson’s Disease. While the supply of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide is a major function of red cells, red cells nevertheless serve many other functions, including Complement regulation. Comparative proteomic inventories have yielded new clues to the processes that regulate red cell membrane–cytoplasm interactions in health and disease, and to the ways by which red blood cells communicate with their environment. In addition, proteomic data have revealed that many unsuspected metabolic processes are active in the red blood cell cytoplasm. Metabolomic studies have confirmed and expanded this notion. Taken together, red cells are at the convergence of many cellular and extracellular events to which all blood-borne processes come together.
Challenge
Red cells circulate in two different sub-populations because during maturation, red cells undergo a series of differentiations. Up until late normoblast, the stages of development all occur within the bone marrow. At this stage the nucleus is expelled and the cells become reticulocytes and are released from the bone marrow. After one to two days, these ultimately become "erythrocytes" or mature red blood cells.
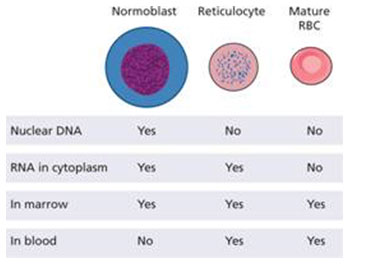 Mature red blood cells (RBCs) are far more abundant; only 0.5-1.5% of circulating red blood cells are reticulocytes. However, reticulocytes possess remnants of translational machinery such as polyribosomes; mature RBCs do not. Reticulocytes can be separated from mature red blood cells based on differences in density, or through immunoaffinity to cell surface proteins, i.e., CD71. Such cell separations can help for example, in the investigation of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium vivax, as it preferentially invades reticulocyte cells in a process that is poorly understood. A proteomic challenge for both cell types however, is the super-abundance of Hemoglobin which accounts for the vast majority, >95% of the protein mass within the cytoplasm. Demonstrable solutions to this challenge are described in the sections to follow. Mature red blood cells (RBCs) are far more abundant; only 0.5-1.5% of circulating red blood cells are reticulocytes. However, reticulocytes possess remnants of translational machinery such as polyribosomes; mature RBCs do not. Reticulocytes can be separated from mature red blood cells based on differences in density, or through immunoaffinity to cell surface proteins, i.e., CD71. Such cell separations can help for example, in the investigation of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium vivax, as it preferentially invades reticulocyte cells in a process that is poorly understood. A proteomic challenge for both cell types however, is the super-abundance of Hemoglobin which accounts for the vast majority, >95% of the protein mass within the cytoplasm. Demonstrable solutions to this challenge are described in the sections to follow.
Red Cells and the Immune Response
Without a nucleus, red cells are exceedingly vulnerable to continuous contact with activated complement proteins in plasma and consequent lysis from the membrane attack complex (MAC). To compensate, they have a different make-up of complement regulators than nucleated cells. One such receptor, Complement Receptor 1 (CR1) regulates complement activation, and the efficient removal of circulating immune complexes by the liver.
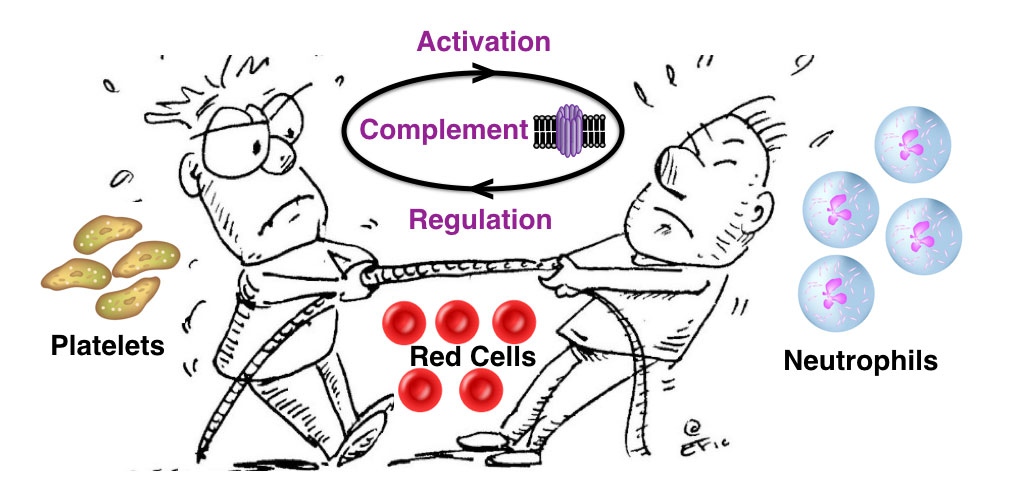
During the innate immune response, red cells can act as an intermediary within the tug-of-war between Platelets and Neutrophils for the localized control and regulation of Complement.
Loss of receptors such as CR1, reduced 3.5 fold, occurs during reticulocyte maturation, when the RBC membrane goes through intense remodeling. In disease, the CR1 copy number per RBC is reduced in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), cold agglutinin disease, Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria, hemolytic anemia, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, and some malignant tumors. Thus, altered CR1 levels can be due to genetic variations or be an acquired phenomenon. As a result, increased complement activation or decreased complement regulation may result in red cell dysfunction. This may explain some of the clinical symptoms seen in severe COVID-19 patients- low oxygen levels and neurological complications.
There is still so much to learn about RBCs, with so many RBC proteins of unknown function. Some of these may be residual proteins, left over from reticulocyte maturation. Others have roles that have yet to be ascertained. Quantitative proteomics studies, using sorted erythrocyte and reticulocyte populations, begin to provide a more accurate picture of the red cell proteome, offering much insight into aging, infectious disease and inflammation.
Solution
Lacking a nucleus, RBCs are unable to synthesize new proteins in response to outside stimuli, making RBCs important reservoirs for biomarker research. Any changes in the RBC proteome content or structure due to disease, should be discernible once a baseline of normal/healthy controls is established. While many proteomic efforts have focused on the red cell membrane content, less attention has been paid to the cytoplasmic fraction, mostly due to the presence of the super-abundance of hemoglobin. This is no longer an impediment to biomarker research on red cell lysates. BSG products have now been demonstrated to efficiently remove hemoglobin from both reticulocyte and mature erythrocyte lysates, enabling such in depth proteomic investigations to flourish.
Outcomes
As one of the key
BSG Advantages, Enrichment/Depletion, BSG offers a choice of two strategies for proteome enrichment, to get the best results: either selectively binding high abundance proteins (the “Bind” products), or choosing not to bind (the “Void” products) thereby enriching the underlying proteome.
HemoVoid™, is designed to remove hemoglobin from erythrocyte lysates in a simple and efficient manner, through a negative selection strategy, meaning the Hemoglobin voids out through the beads, and the vast majority of the remaining proteome binds to the beads. For subsequent analysis, the bead-bound enriched proteome can either be eluted, or for LC-MS/MS, digested on-bead. This latter process is called Bead-assisted Sample Prep or BASP™.
HemogloBind™, binds hemoglobin, with a high degree of selectivity that does not cross-react with most other red cell and serum components. It is available as either a suspension reagent product or in a dry powder NuGel™-based format. In the former, The suspension product - HemogloBind™ is supplied in a bottle and aliquoted at suitable v/v ratios depending upon the Hemoglobin concentration. In the NuGel™ powder format, the powder is first weighed and dispensed into SpinX filters according to use guidelines supplied with the product.
These journal reports describe the utility of BSG’s Hemoglobin Removal products in the proteomic analysis of red cells.
Human Proteome Project - Annotation of Erythrocytes
HemoVoid™ “protein-level pre-fractionation proved helpful in identifying additional proteins and N-termini”. 778 proteins were identified from the cytosolic fraction, 171 of which were not represented in either the soluble non-depleted fraction or the membrane fraction. LEARN MORE
Malaria infected erythrocytes
The authors describe how P. vivax-infected Retics (iRetics) express human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I), which are recognized by CD8+ T cells and killed by granulysin (GNLY) and granzymes. However, how Plasmodium infection induces MHC-I expression on Retics is unknown. In addition, whether GNLY helps control Plasmodium infection in vivo has not been studied. To remove interferences associated with Hemoglobin, the article states, "For western blot analysis, erythroblasts pellets were resuspended in RIPA Buffer (Sigma)…. The Retics were treated with HemogloBind (Biotech Support Group)...". LEARN MORE
For drug interaction and discovery
"The intact-cell cellular thermal shift assay protocol features a HemogloBind™ - based sample processing step, which provides a relatively fast, reliable and inexpensive method to deplete >90% of hemoglobin…it leads to a 40-50% increase in the number of peptide spectrum matches (PSMs) for P. falciparum and nonhemoglobin human proteins."
LEARN MORE
Reticulocyte transitioning
From a Science article, the study used multiplexed quantitative proteomics to identify candidate substrates of UBE2O, an E2 (ubiquitin-conjugating) enzyme, in an unbiased and global manner. Because of the overly abundant presence of Hemoglobin, "Reticulocytes were lysed...HemogloBind™ suspension was added to the samples, ...The supernatants, which contain hemoglobin-depleted sample, were ... processed for TMT quantification." LEARN MORE
Post-translational modifications in erythrocytic diseases
The study aimed to report the Identity, biological activity and concentration of NG-methylated proteins by using GC-MS and LCMS/MS approaches. The article states "we included in our method the use of HemoVoid to remove specifically most erythrocytic hemoglobin and to improve the SDS-PAGE separation of proteins for further processing. ... removal of hemoglobin by this technique enabled an effective separation by SDS-PAGE and isolation of bands, presumably by avoiding overloading of the gels by hemoglobin." LEARN MORE
In Parkinson's Disease Research
The article describes the advantage of HemoVoid™ in detection of low abundance proteins when comparing their amounts (in percent) between four alternative extraction conditions, stating "... Most peptides, following HemoVoid™ extraction, showed ion abundances ranging between 1.00E+5 and 1.00E+6 (31%). In comparison to this, fewer peptides (10–23%) were within this range following extraction with all other protocols". With respect to potential biomarkers for Parkinson’s Disease, the article states "For example, PRDX6 accounts for 0.4% of the total ion abundance after DOC (deoxycholate) extraction, whereas following HV (HemoVoid™) extraction, this increases to 8%, a 20-fold enrichment". The article describes methods to digest the HemoVoid™ bead-bound proteome, greatly simplifying the workflow for LC-MS/MS analysis. LEARN MORE
The goal of this study was to determine whether blood cells expressing α-Synuclein can differentiate Parkinson’s disease (PD) from healthy controls. Two proteoforms - PSer129 a-Syn (phosphorylated pathological form in Lewy bodies) and Oxidized a-Syn levels are observed in blood cells, but both at considerably lower concentration than total a-Syn, so the extremely high abundance of hemoglobin interferes with their analysis. To compensate, the article states for PSer129 α -Syn & Oxidized α -Syn detection by immunoassay, "followed from hemoglobin clearance with HemoVoid kit...".
LEARN MORE
In Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) Research
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) is a rare comorbidity in colorectal cancer (CRC) and has an unknown etiology. To better understand cancer-related anemia, the authors’ investigated ectopic band 3 expression and erythrocyte membrane-bound IgG in a CRC cohort. To reduce the interference from Hemoglobin, the article states "Erythrocytes were lysed ... and hemoglobin was depleted using HemoVoid". LEARN MORE
In Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Research
Using proteomics-based evaluation of red blood cells (RBC), the authors identified differentially abundant proteins associated with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSA). Proteome variations between various time points were assessed. The article states "RBC cytoplasmic fraction depleted of hemoglobin, using HemoVoid™ system, were analyzed by two-dimensional fluorescence difference gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE), the 2D image software-based analyzed and relevant differentially abundant proteins identified by mass spectrometry (MS)". LEARN MORE
Additional Key Advantages of HemoVoid
™
- Consumable, cost-effective
- Hemoglobin voids in flow-through >98%, with <30 minute bind/wash/elute protocol
- Suitable for high-throughput quantitative analysis
- Sample types include red blood cells, whole blood, and dried blood cards
- Species agnostic, validated on human, mouse, sheep, goat, bovine
- Eluted proteins maintain their tertiary structure and functional characteristics and can be profiled by native PAGE, structural activity probes, or enzymatic assay
Additional Key Advantages of HemogloBind
™
- Consumable, cost-effective
- Has a high degree of specificity for hemoglobin, binding up to 10 mg/ml
- Applications in enzyme analysis and analytical interferences
- Species agnostic, validated on human, mouse, sheep, bovine, goat, fish
- Removes hemoglobin from whole blood lysates, dried blood cards, organs, tissues, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF)
- The flow-through unbound fractions maintain their tertiary structure and functional characteristics and can be profiled by native PAGE, structural activity probes, or enzymatic assay
Click here for our complete line of Hemoglobin Removal products.
More Resources
Case Study: The Potential for New Blood Biomarkers in the Management of COVID-19 Disease - Unleashing the Power of Proteomics To Better Understand the Innate Immune Response to Infectious and Non-infectious Inflammatory Stimuli. LEARN MORE
BIOTECH SUPPORT GROUP LLC and PRO TEST DIAGNOSTICS AB Enter Supply Agreement for HemoVoid™ for Blood Doping Tests
 Biotech SupportGroup (BSG, Monmouth Junction, NJ) and Pro Test Diagnostics AB (Umeå, Sweden) jointly announce that they have entered a supply agreement for the BSG product HemoVoid™. BSG produces products for simple and efficient removal of hemoglobin from red cell lysates. Pro Test Diagnostics AB is a developer of rapid and accurate detection of blood doping through molecular fingerprints. LEARN MORE Biotech SupportGroup (BSG, Monmouth Junction, NJ) and Pro Test Diagnostics AB (Umeå, Sweden) jointly announce that they have entered a supply agreement for the BSG product HemoVoid™. BSG produces products for simple and efficient removal of hemoglobin from red cell lysates. Pro Test Diagnostics AB is a developer of rapid and accurate detection of blood doping through molecular fingerprints. LEARN MORE
Download Whitepaper entitled "Hemoglobin Removal - The Gold Standard Products"
|