Publications
& Reports A>Z
Stroma
Liquid Biopsy™ Whitepaper-January
2022
This
whitepaper highlights the importance of the systemic inflammatory
response to the presence of cancer anywhere in the body. It also
describes how the vast circuitry of cascading proteolytic events,
requires suitable regulation in order to resolve innate immunity and
accommodate the adaptive T-cell response
in cancer. From this, new strategies for more durable therapeutic
efficacy will be uncovered.
Biotech Support Group and Leiden University Medical Center Report on a Gene Signature Ratio derived from Stroma Liquid Biopsy™ that Predicts Survival in Colon Cancer
Ravensbergen, Cor J., et al. "The Stroma Liquid Biopsy Panel Contains a Stromal-Epithelial Gene Signature Ratio That Is Associated with the Histologic Tumor-Stroma Ratio and Predicts Survival in Colon Cancer." Cancers 14.1 (2022): 163.
Liquid biopsy has emerged as a novel approach to tumor characterization, offering advantages in sample accessibility and tissue heterogeneity. However, as mutational analysis predominates, the tumor microenvironment has largely remained unacknowledged in liquid biopsy research. The Stroma Liquid Biopsy™ (SLB) proteomics panel comprises a set of 13 proteins from interconnected stromal pathways (i.e., coagulation, complement, acute phase inflammation) and is believed to capture a plasma proteomic blueprint indicative of a deranged systemic response in cancer. As such, it encompasses the importance of the tumor microenvironment (TME) compartment in liquid biopsy. Within similar context, the histologic tumor-stroma ratio (TSR), a stroma-derived biomarker developed by LUMC, has been validated as an independent predictor of patient survival in various primary tumor types. The current work provides an explorative gene transcriptomic characterization of the SLB proteomics panel in colon carcinoma by integrating single-cell and bulk transcriptomics data from publicly available repositories.
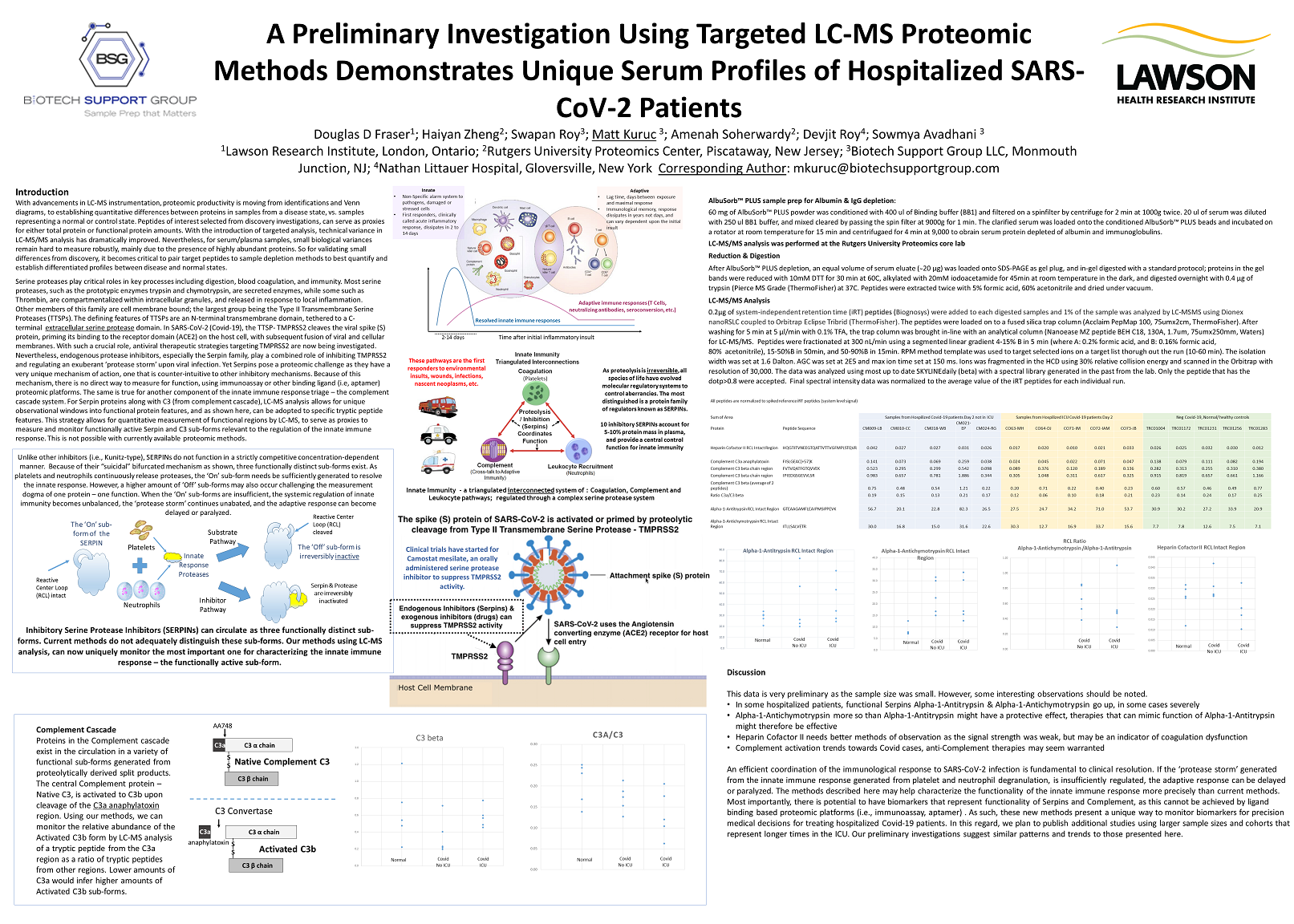
A
Preliminary Investigation Using Targeted LC-MS Proteomic Methods
Demonstrates Unique Serum Profiles of Hospitalized SARS-CoV-2
Patients
Douglas
D Fraser
1;
Haiyan Zheng
2;
Swapan Roy
3; Matt
Kuruc
3;
Amenah Soherwardy
2;
Devjit Roy
4;
Sowmya Avadhani
3
1Lawson
Research Institute, London, Ontario;
2Rutgers
University Proteomics Center, Piscataway, New Jersey;
3Biotech
Support Group LLC, Monmouth Junction, NJ;
4Nathan
Littauer Hospital, Gloversville, New York
Corresponding
Author
:
mkuruc@biotechsupportgroup.com
Brief
description: For serum samples, targeted LC-MS is challenging, mainly
due to the presence of highly abundant proteins. So it becomes
critical to pair target peptides to sample depletion methods to best
establish differentiated profiles between samples. In this
preliminary investigation, we use unique methods described here to
characterize the functionality of the innate immune response in
hospitalized Covid-19 patients, more precisely than current methods.
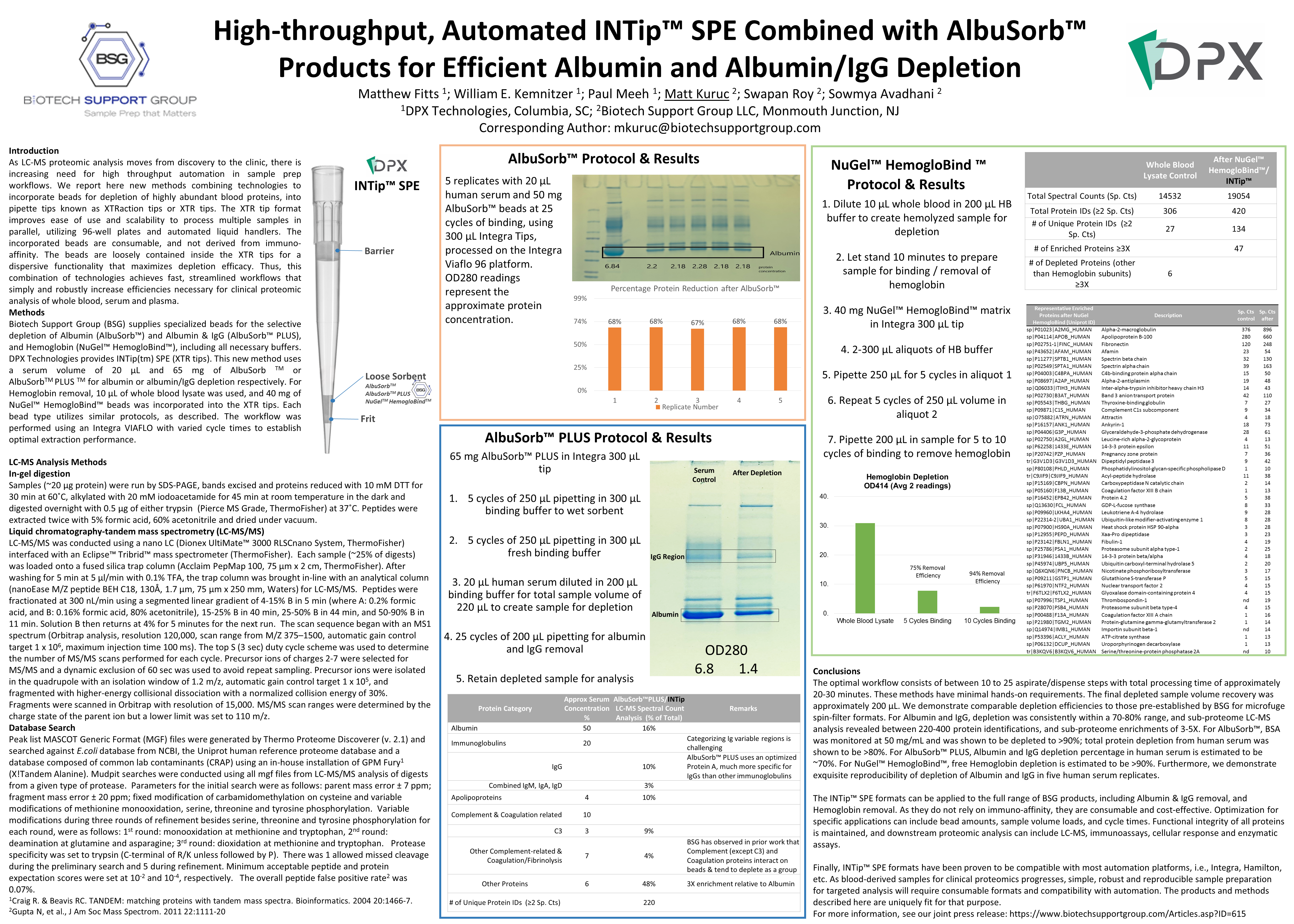
High-throughput,
Automated INTip™ SPE Combined with AlbuSorb™ Products for
Efficient Albumin and Albumin/IgG Depletion
Matthew
Fitts
1;
William E. Kemnitzer
1;
Paul Meeh
1; Matt
Kuruc
2;
Swapan Roy
2;
Sowmya Avadhani
2
1DPX
Technologies, Columbia, SC;
2Biotech
Support Group LLC, Monmouth Junction, NJ
Corresponding Author:
mkuruc@biotechsupportgroup.com
Brief
description: We report here new methods to incorporate beads for
depletion of Albumin, IgG and Hemoglobin, into pipette tips known as
XTRaction tips or XTR tips. The XTR tip format improves ease of use
and scalability to process multiple samples in parallel, utilizing
96-well plates and automated liquid handlers. The incorporated BSG
beads are consumable, and not derived from immuno-affinity.
“These
two posters highlight the value of collaborative partners jointly
working to commercialize new methods and biomarkers using novel
proteomic sample prep products. The first demonstrates how we can
adapt LC-MS to study the functionality of a most important regulating
family of proteins - the Serpins, as they serve as central control
within the innate immune response. The second demonstrates our
commitment to high-throughput and automation for clinical proteomics.
It is very exciting to share these developments with a dedicated
group at the forefront of mass spectrometry research”, states Dr.
Swapan Roy, Ph.D., President and Founder of Biotech Support Group.
Journal
Publications
Albumin
Removal Kits
Serum
Swapan Roy, Matthew Kuruc. The Functional Subproteomes of Serpin Protease Inhibitors are Now Open for LC-MS Biomarker Discovery. MOJ Proteomics Bioinform 2016, 3(6): 00106
The authors consider that the conformational variants of the unique family of protease inhibitors annotated as SERPINs, are most often underrepresented in proteomic analyses. This limits understanding the complex regulation that this family of proteins presents to the networks within the protease web of interactions. Using bead-based separation provided by the NuGel™ family of proteomic enrichment products - notably AlbuVoid™ & AlbuSorb™, the authors demonstrate their utility to satisfy investigations of serum SERPINs. The authors also suggest their use to develop functional profiles of the SERPIN Proteoform, and how those can establish relationships to disease phenotypes, gene mutations, and deregulated mechanisms.
Featured Application - Functional Proteomics
Sun, Zhenyu, Xiaofeng Chen, Gan Wang, Liang Li, Guofeng Fu, Matthew Kuruc, and Xing Wang. "Identification of functional metabolic biomarkers from lung cancer patient serum using PEP technology." Biomarker Research 4, no. 1 (2016): 1.
Zheng
et al.
AlbuVoid™
Coupled to On-Bead Digestion - Tackling the Challenges of Serum
Proteomics
. J
Proteomics Bioinform 2015, 8:9
Abstract
For
cancer research, serum and plasma are especially attractive sample
types as collection of blood is common, simple and only minimally
invasive. Yet serum samples can offer unique challenges in LC-MS
proteomic analyses. The two biggest challenges being: 1) the high
abundance of Albumin accounting for about 50% of the total protein
mass and, 2) proteolytic resistance, in large part due to substantial
amount of glycoprotein, a modification that manifests proteolytic
resistance. In this short report, we describe new methods using a
surface/bead based product, AlbuVoid™, which depletes Albumin
through a negative selection or voidance strategy, retaining the vast
amount of the remaining serum proteome on the bead. We then combine
this novel enrichment, with a direct and seamless integration with
Trypsin digestion, a method conventionally referred to as on-bead
digestion. We evaluated the digestion time as a parameter to identify
whether different sub-populations of peptides and proteins can be
observed by LC-MS analyses. Using 2 different allotted digestion
times - 4 hours, and overnight, each with a singular 3 hour gradient
LC-MS run, between 400-500 total proteins were observed for both
human and rat sera, with overlapping and distinct sub-populations
observable at each digest time. These results support that the
described methods gain efficiencies over other high abundance
depletion and in-solution digestion workflows. We solicit that such
workflows will minimize many of the inconsistencies of proteolytic
hydrolysis for both discovery and quantitative serum proteomic
applications.
In
this short case study, the enrichment of select sub-populations of
proteins is beneficial to systematically analyze protein functions of
a whole enzyme family from an entire proteome. AlbuVoid™ was used
to remove Albumin and enrich the low abundance proteome, noting that
distinguishable activity features are presented from the lung cancer
vs. the normal sera. KinaSorb™ was used to enrich for both a narrow
spectrum substrate profile—Hexokinase activity, and a
broad-spectrum protein kinase activity. The number of observable
features was consistent with such narrow and broad-spectrum
activities. AlbuVoid™enrichment and PEP processing proved suitable
for profiling the functional activities of Hexokinase, Protease and
Alkaline Phosphatase. These enzyme feature profiles are indicative of
the functional diversity that can be generated, annotated and
compared within and between sample phenotypes, using the combined
methods.
Application
Reports
Albumin
Removal Application Report.
From
a foundational NuGel™ platform chemistry, a library of bead
architectures has been created to support proteomic enrichment. These
beads are general non-specific protein adsorbents, or stated another
way - beads with weak affinity or imperfect fit interactions. Two of
our products support Albumin Removal: AlbuSorb™ for selective
binding of Albumin & AlbuVoid™ for negative selection or
voidance of Albumin with consequent enrichment of the remaining serum
proteome on the bead. We now report on adding Immunoglobulin
depletion as an extension to AlbuSorb™. A LC-MS/MS analysis on
human serum revealed between 500-600 total proteins, many of which
are qualitatively and quantitatively biased to sub-proteomes either
depleted of Immunoglobulins, or not depleted of Immunoglobulins.
AlbuSorb™ PLUS designates and distinguishes AlbuSorb™ without
immunoglobulin depletion, from AlbuSorb™ with Immunoglobulin
depletion. Here we compare proteomic data derived from AlbuSorb™,
AlbuSorb™ PLUS (which includes Immunoglobulin depletion), and
AlbuVoid™.
Albumin
Removal Reference Applications
Two NuGel™ based products support
Albumin Removal:
Cleanascite™
- Lipid Removal and Cell Response Applications
The
“omics” revolution demanded new and different sample prep
separations that were not efficiently performed by conventional
technologies. While effective for many applications, these tools were
not efficient for “omics” sample preparation, as
throughput, economy and simplicity are especially required.
Furthermore, these same separation tools often denatured proteins
which limited there use in applications which demanded the
measurement of function, structure or bio-activity. For these
reasons, BSG has been dedicated to create new methods and
applications to drive efficient workflows and better data quality for
all proteomic and biomarker analyses. Of special importance is the
value created when certain families of biomolecules can be evaluated
with respect to cell response and viability. For example,
extracellular vesicles (EVs) substantially influence cultured cell
behavior. While all of our products serve cell response applications,
we report here an extensive list of applications in this area for
Cleanascite™. Cleanascite™ is derived through a
proprietary formulation of metallic oxide derivatives. However,unlike
other metallic oxides, Cleanascite™ does not have significant
protein binding, making its selectivity profile for lipids un-rivaled
in the bio-research products industry. As a result, it is ideal to
clear lipid-associated matrix effects - including extracellular
vesicles, which may influence cell response assays.
To
download whitepaper entitled “Cleanascite™ - Lipid
Removal and Cell Response Applications"
Visit:
http://www.biotechsupportgroup.com/v/vspfiles/templates/257/pdf/CleanasciteCellResponseReferenceApplications121218.pdf
Cleanascite™
is derived through a proprietary formulation of metallic oxide
derivatives. Unlike other metallic oxides, Cleanascite™ does not
have significant protein binding making its selectivity profile for
lipids unique in the bio-research products industry.
The applications and references for use of Cleanascite™ are described in this downloadable report.
Functional
& Chemical Proteomics
Mutations,
post-translational modification, and non-covalent binding factors all
play a role in fine tuning polypeptide sequence to final function.
Because of this phenomena, populations of proteins annotated to the
same sequence nevertheless can display multiple functions within
tissues and disease states. Likewise, the same or similar function
may be presented by multiple sequences, with subcellular control
mechanisms regulating functional diversity. As a consequence,
strictly abundance based biomarkers may lack the necessary dynamic
range and greater specificity provided by functional based
biomarkers, to define the phenotype. Thus, Functional Proteomic
techniques such as described here, support a top-down proteomic
strategy starting with functional annotation of the structurally
intact protein, and ending with sequence and structural annotation.
Journal
Publications
C
Wan,
B
Borgeson
, S
Phanse
,
F Tu,
K
Drew
, G
Clark
,
et al.
Panorama
of ancient metazoan macromolecular complexes
.
Nature Volume:525, Pages:339–344 Date published:(17 September
2015).
doi:10.1038/nature14877
Two
of BSG products,
NRicher™ 6 and HemogloBind™, were able to
contribute to this rigorous examination of protein complexes. When
our products were used as a pretreatment step in the overall
workflow, about twice the number of observations and annotations
became possible. This further validates that the sub-proteome bias
characteristics of
NRicher™ 6 can simplify complex proteomes into
less complex sub-proteomes with efficiencies suitable for deep
functional proteome characterization. Furthermore, this study
demonstrated the importance of a key feature implicit to all of our
products; that is the maintenance of functional and structural
integrity after separations. Without that particular feature, these
additional observations would not have been possible.
Most
efforts in proteomics seek to identify and sequence annotate the
proteome by LC-MS/MS analyses of peptides derived through proteolytic
processing of the parent proteome. However, little attention has been
paid to functional annotation. Yet functional annotation is crucial
as the landscape of protein conformations is highly variable, and
each conformation may contribute to its own unique activity. To
overcome inefficiencies in functional annotation, a new method
combining the enrichment attributes of Biotech Support Group
products, along with the PEP platform developed by Array Bridge (St.
Louis, MO) is described. The PEP technology is a top-down method
which starts with functional annotation and ends with sequence and
structure information. It is based on a modified 2D Gel
Electrophoresis to separate proteomes, electro-eluting from the PEP
plate and systematically measuring enzyme activities from 384
microwell plates.
Elastin
as a Marker
. Cosmetics
and Toiletries Vol. 129, No. 7, September 2014.
There
is general agreement on elastin’s role in skin health, aging and
appearance, but no method has yet elucidated how it degrades with
aging when challenged by sun exposure or other means.This paper
reviews two inconsistent theories in the literature, degradation and
buildup, and highlights potential methods to marry the two. It also
suggests proteomics as a method for further investigation.
NuGel™ surface
platform was applied to these publications
Functional Proteomic
Profiling of Phosphodiesterases
International
Journal of Proteomics. Volume 2012, Article ID 515372, 8
pages.
doi:10.1155/2012/515372.
The
surface chemistries reported here as SeraFILE in this article form
the basis of the product NRicher™ 6.
Functional
proteomic profiling can help identify targets for disease diagnosis
and therapy. Available methods are limited by the inability to
profile many functional properties measured by enzymes kinetics. The
functional proteomic profiling approach proposed here seeks to
overcome such limitations. It begins with surface-based proteome
separations of tissue/cell extracts, using SeraFILE, a proprietary
protein separations platform. Enzyme kinetic properties of resulting
subproteomes are then characterized, and the data integrated into
proteomic profiles. As a model, SeraFILE-derived subproteomes of
cyclic nucleotide-hydrolyzing phosphodiesterases (PDEs) from bovine
brain homogenate (BBH) and rat brain homogenate (RBH) were
characterized for cAMP hydrolysis activity in the presence (challenge
condition) and absence of cGMP. Functional profiles of RBH and BBH
were compiled from the enzyme activity response to the challenge
condition in each of the respective subproteomes. Intersample
analysis showed that comparable profiles differed in only a few data
points, and that distinctive subproteomes can be generated from
comparable tissue samples from different animals. These results
demonstrate that the proposed methods provide a means to simplify
intersample differences, and to localize proteins attributable to
sample-specific kinetic responses. It can be potentially applied for
disease and non-disease sample comparison in biomarker discovery and
drug discovery profiling.
Poster
reprint first presented at US HUPO April 6-8, 2014.
Review
Reports
Hemoglobin
Removal Reference Applications
Three
BSG products support Hemoglobin Removal applications:
-
HemogloBind™
& NuGel™ HemogloBind™ for selective binding of Hemoglobin &
-
HemoVoid™
for negative selection or voidance of Hemoglobin with consequent
enrichment of the remaining erythrocyte proteome on the bead
There
are many DNA, RNA, and nucleic acid preparation products that serve
the market well for most applications. Most of these products in some
way utilize a bind/wash/elute strategy adopting surface reagents such
as silica & metallic oxides and similar solid-phase
chemistries.However, there still remain situations when these
products are not optimal. This Handbook serves to guide users in the
use of ProCipitate™ when the “other kits don’t fit”.
The
ProCipitate™ strategy is opposite to common prep strategies, as
instead of binding nucleic acids, the protein is efficiently depleted
with no interaction with the soluble nucleic acids. ProCipitate™ is
offered in a variety of kits, providing all necessary buffers and
accessories for different applications: ProPrep™ Genomic 96/100 for
high throughput whole blood DNA; ProPrep™ BAC Mini for large insert
plasmid preps.
|