AlbuVoid™ Workflows Advance Cell Secretome Proteomics
BACKGROUND
A significant portion (~ 13–20%) of the human proteome consists of secretory proteins (the secretome), a collection of proteins consisting of truncated transmembrane proteins and proteins secreted by cells into the extracellular space. The secretory proteins play important roles in cell migration, signaling and communication. As the secretome regulates a multitude of biological and physiological processes, it is an important source for potential clinically accessible biomarkers.
As a result, studies of the cell secretome have greatly increased in recent years owing to improvements in proteomic platforms, and mass spectrometry instrumentation. This has led to reports observing alterations in the type and abundance of secretome proteins from cell culture models of many diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders
CHALLENGE
The secretome workflow involves stepwise processes such as the collection of conditioned medium (CM), concentration and sample prep of the CM, LC-MS analysis, database spectral analysis, and filtering and comparing of secretory proteins. Within this workflow however lies a major challenge; the inherent sensitivity of LC-MS to assess the wide dynamic range for the low abundance of genuine secreted proteins, over the highly abundant proteins derived from the serum containing media, the preponderance of which is bovine serum albumin (BSA). LC-MS signal derived from BSA in cell culture secretomes can be as high as 50% of the analysis, masking the underlying proteome of interest.
Some strategies include incubation using serum-free media before harvesting the secretome. However, serum-free media often distorts the cell secretory protein profile owing to poor cell viability. A simple workflow for secretome analysis from serum-containing media is therefore highly desirable.
SOLUTION
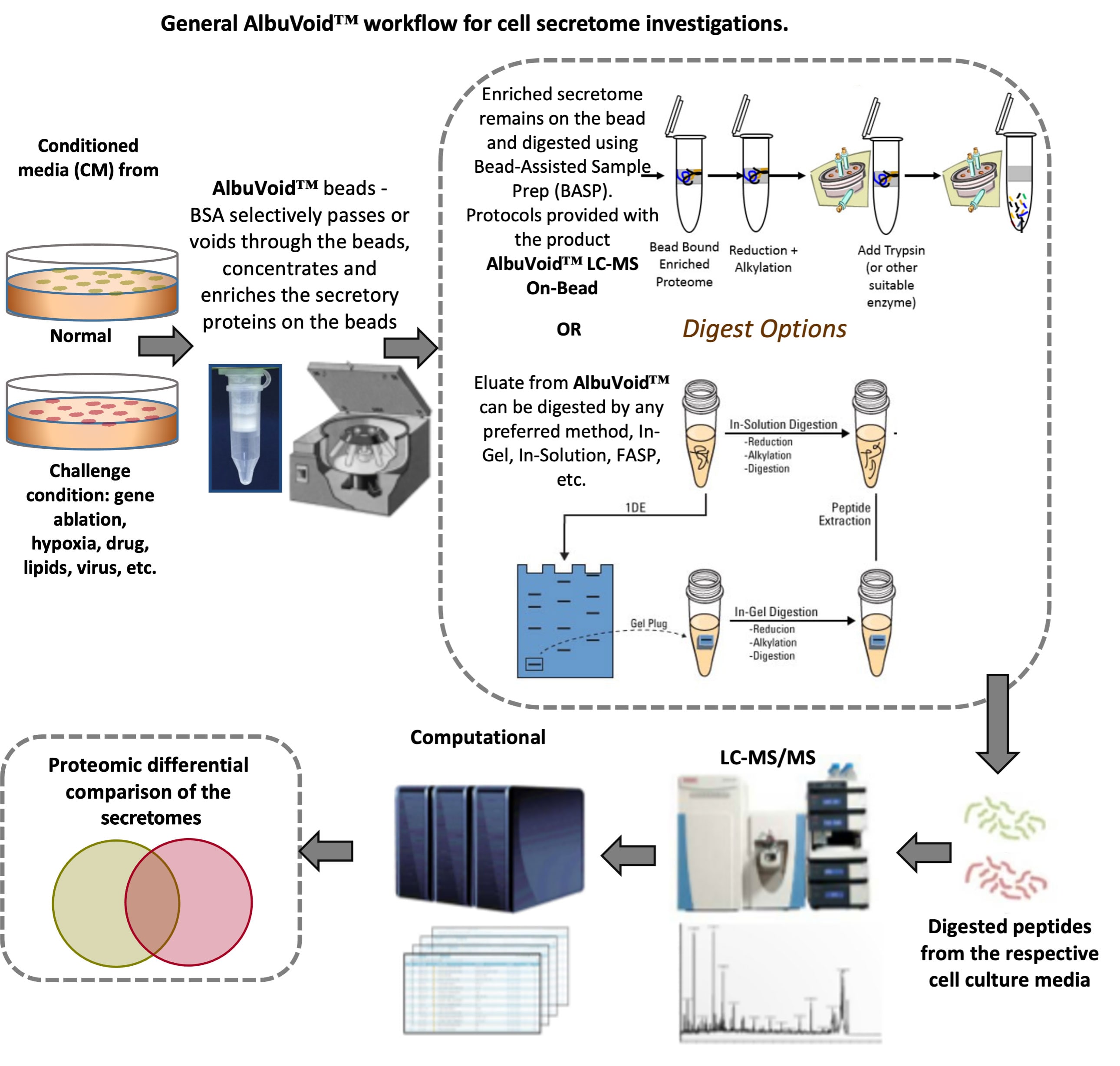
The secretome can be simply and efficiently depleted of BSA by the product AlbuVoid™. AlbuVoid™ has virtually no affinity for Albumin and so Albumin passes or voids through the beads. The vast majority of the remaining secretome gets bound to the beads, see workflow Figure. This offers many advantages for secretome analysis:
- Depletion of BSA to improve the coverage of the secretome
- Concentration of the BSA-depleted secretome proteins on the beads and the removal of other media contaminants
- Many options for digestion, including our Bead-assisted Sample Prep (BASP) method, whereby no elution is necessary; the digestion is done on-bead, greatly simplifying the process. Protocols for this methods are included in our AlbuVoid™ LC-MS On-bead product.
EXAMPLE OUTCOMES USING ALBUVOID™ FOR CELL SECRETOMES
 Jenull, Sabrina, et al. "The histone chaperone HIR maintains chromatin states to control nitrogen assimilation and fungal virulence." Cell Reports 36.3 (2021): 109406. Jenull, Sabrina, et al. "The histone chaperone HIR maintains chromatin states to control nitrogen assimilation and fungal virulence." Cell Reports 36.3 (2021): 109406.
The authors report a pivotal role for the HIR histone chaperone complex in modulating virulence of the human fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Genetic ablation of HIR function alters chromatin accessibility linked to aberrant transcriptional responses to protein as nitrogen source. This accelerates metabolic adaptation and increases the release of extracellular proteases, which enables scavenging of alternative nitrogen sources. The article states for “Cell-free supernatants from 16 hours YNB-BSA (0.025% BSA) cultures grown at 30°C were used for Mass-Spec analysis. Collected supernatants were lyophilized and dissolved in 400 μl of water for AlbuVoid™ treatment for albumin depletion…Albumin-free enriched secretory proteome was eluted from beads” This work provides mechanistic insights into chromatin-coupled regulatory mechanisms that fine-tune pathogen gene expression and virulence.
 Narain, Niven Rajin, Rangaprasad Sarangarajan, and Vivek K. Vishnudas. "Interrogatory cell-based assays for identifying drug-induced toxicity markers." U.S. Patent Application No. 16/180,446. Narain, Niven Rajin, Rangaprasad Sarangarajan, and Vivek K. Vishnudas. "Interrogatory cell-based assays for identifying drug-induced toxicity markers." U.S. Patent Application No. 16/180,446.
The lack of reliable tools that can help with predicting toxicity early in drug development is partly to blame for a 90% attrition of potential compounds entering clinical development, 30% of which is owing to poor clinical safety. Cardiotoxicity particularly is a leading cause of drug withdrawal. The patent application states “In one embodiment, the cells can be cultured in serum containing medium: …Serum albumin can be depleted from all samples using AlbuVoid column (Biotech Support Group, LLC) following the manufacturer's instructions with the modifications of buffer-exchange to optimize for condition medium application.” The invention described is useful for identifying markers associated with drug-induced toxicity.
OTHER RESOURCES
Selectively Voids Albumin, Binds Low Abundance Proteome
- Albumin voids in flow through, >95%
- <30 minute protocol
- Low abundance enrichment
- On-bead digestion protocols, efficient LC-MS workflows
- Consumable, cost-effective, no column regeneration or cross-contamination
AlbuVoid™ LC-MS On-Bead
Selectively Voids Albumin, Binds Low Abundance Proteome for Bead-assisted Sample Prep (BASP) digestion
- Seamless workflow
- Label, label free & glyco- compatible
- Unique proteolytic efficiencies

Using 2 different allotted digestion times - 4 hours, and overnight, each with a singular 3 hour gradient LC-MS run, between 400-500 total proteins were observed for both human and rat sera, with mostly overlapping but also with distinct sub-populations observable at each digest time. These results support that the described methods gain efficiencies over antibody depletion and in-solution digestion workflows, for both discovery and quantitative serum proteomic applications.
|