|
Cleanascite™ Use Helps Identity a Distinct Cancer-cell Lipid Metabolism Archetype In this study, researchers have uncovered critical mechanisms driving immune suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), highlighting the role of oxidized LDL (oxLDL) in promoting protumor macrophage polarization. Press Release
Cleanascite™
Use Helps Identity a Distinct Cancer-cell Lipid Metabolism Archetype
MONMOUTH
JUNCTION, NJ, July 25, 2025
— In this study, researchers have
uncovered critical mechanisms driving immune suppression in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), highlighting the role of oxidized LDL
(oxLDL) in promoting protumor macrophage polarization. Central to the
The study, entitled “ Metabolism archetype cancer cells induce protumor TREM2+ macrophages via oxLDL mediated metabolic interplay in hepatocellular carcinoma ” and conducted by an international team led by Fudan University, identified a distinct "metabolism archetype" of cancer cells characterized by high lipid metabolism and cholesterol biosynthesis. These cancer cells generate oxLDL, which in turn polarizes TREM2+ tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) via the TREM2–SYK–CEBPα signaling axis. This interplay results in immune suppression and resistance to immunotherapy in both human and mouse models of HCC.
Cancer
cells often display a
“
It
is very rewarding to see how this study not only sheds light on the
immunometabolic dynamics of hepatocellular carcinoma, but potentially
towards novel therapeutic approaches that target metabolic crosstalk
between cancer cells and immune cells. Importantly, the study
underscores the growing importance of Cleanascite™ in advancing
cancer metabolism and tumor microenvironment research.,” stated Dr.
Swapan Roy, President and Founder of Biotech Support Group. “Unlike
traditional solvent-based methods, Cleanascite™ provides an
aqueous, cell-compatible reagent, preserving cellular function and
phenotypic integrity after removal of lipids. With such
compatibility in live cell models, Cleanascite™ enables researchers
to confidently dissect the complex roles of lipid metabolism in
disease mechanisms.”
For
additional product details, visit:
About
Biotech Support Group LLC
For
Business Development Inquiries:
|

- About
- Products
- Hemoglobin Removal Kits
- Lipid Removal & Clarification
- Urine Protein & Low Abundance Enrichment
- Class Specific Enrichment
- Sample Prep Mass Spectrometry
- Functional & Chemical Proteomics
- Genomic Sample Prep
- Accessories
- Technical Resources
- References
- Publications & Reports
- FAQs
- Case Studies
- Cleanascite™ Unlocks Insights into Lipid-Driven Tumor Immunosuppression
- NRicher™ Bead Platform Provides Unique Sub-Proteome Biases And Fit For Purpose Opportunities for Targeted LC-MS Quantification
- BSG Products To Assist in Analyzing Macrophage Polarization
- Ectodomain Shedding and Enrichment of the Soluble Membrane Proteome
- Investigate out of the Venn Diagram box
- Methods to selectively deplete or purify Hemoglobin from Dried Blood Spots (DBS)
- The Utility of HemoVoid™ is Demonstrated in 3 Proteomic Investigations Identifying Potential Disease Specific Biomarkers
- The 4 common features of our sample prep products, known as the BSG Advantage, are highlighted in a selection of journal references.
- AlbuVoid™ Workflows Advance Cell Secretome Proteomics
- Lipid Removal for Phenotypic Cell Response in Cancer Research
- The Influence of Sample Prep Bias on LC-MS Targeted Peptide Quantification in Serum Proteomics
- Re-imagining proteomics for developing precision medicine biomarkers of the innate immune response in SARS-CoV-2
- Patent Application Describes New Proteomic Methods to Monitor Protease Inhibitor Function During Covid-19 Infections
- Efficient Hemoglobin Removal Advances Red Cell Proteomics Offering Many New Insights Into Inflammation and Infectious Disease
- The Potential for New Blood Biomarkers in the Management of COVID-19 Disease
- Establishing the Utility of HemoVoid™ and HemogloBind™ as Enrichment Tools for Proteomic Analysis of Red Cells and Whole Blood in Parkinson’s Disease
- Species Diversity Supported By BSG Products
- Poster Report Describes Loss of Functional Serpin Activity In Cancer Patient Blood
- AlbuVoid™️ PLUS & AlbuSorb™️ PLUS Evaluating Different Windows of Observation Solves The Many Challenges of Serum Proteomics
- Tackling the Challenges of Serum Proteomics
- Lipid Removal Sample Prep for Cell Response Applications
- Sample Prep for Proteomic Analysis of Saliva
- Biotech Support Group Featured in Book, "Functional Proteomics – Methods and Protocols"
- Sample Prep Liquid Biopsy Products Suitable for Proteomic Profiling of a Variety of Body Fluid Sample Types
- Albumin and High Abundance Depletion
- Using HemogloBind™ as a Hemoglobin Binding Reagent
- Diverse technologies available for researchers to selectively bind or enrich exosomes and extracellular vesicles.
- Stroma Liquid Biopsy™ Biomarkers Profile Pan-Cancer Dysregulation of the Serum Proteome
- Diverse Depletion and Enrichment Technologies Enhance Simplicity and Efficiency of Obtaining Quality Proteomic Information
- Use On-Bead Digestion to Improve Time Required for Serum Digestion
- Using AlbuVoid™ as a Serum Protein Enrichment Kit in Functional Proteomics
- Using Cleanascite™ as a Lipid Absorption and Clarification Reagent
- Using HemoVoid to Remove Hemoglobin Before Analysis
- Blog
- Contact
- Liquid Biopsy
 study's methodology was the use of
Cleanascite™, a
lipid-binding reagent from Biotech Support Group, which enabled the
researchers to efficiently isolate and study lipid-influences from
tumor interstitial fluid (TIF).
study's methodology was the use of
Cleanascite™, a
lipid-binding reagent from Biotech Support Group, which enabled the
researchers to efficiently isolate and study lipid-influences from
tumor interstitial fluid (TIF). 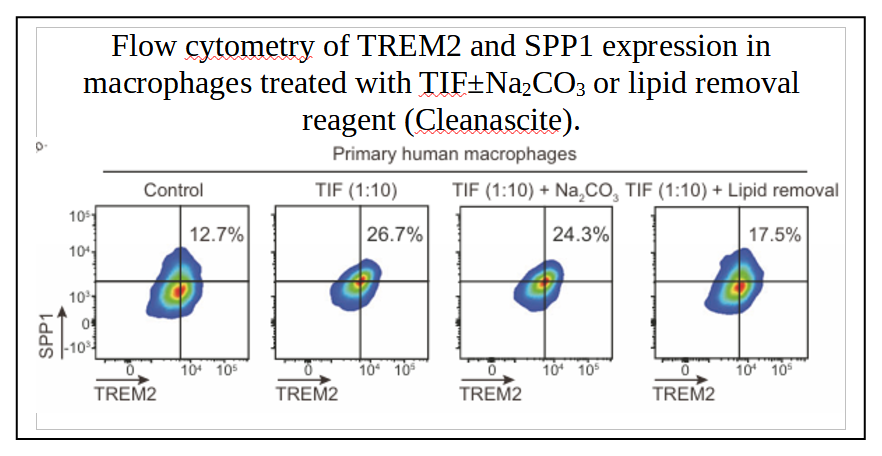 marked upregulation in lipid metabolism, a
mechanism that not only promotes their proliferation but also manipulates stromal cells, like tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs),
contributing to an immuno suppressive tumor microenvironment (TME).
To interrogate the lipidomic environment of the TME, the researchers
utilized Cleanascite™ to selectively remove lipids and confirm the
lipid-dependence of TREM2+ TAM polarization. HCC-derived TIF potently
induced the expression of TREM2 and SPP1 in macrophages, which was
attributed to lipids…(Fig.). Consequently, Cleanascite™ enabled a
more precise functional dependency measurement, strengthening the
study’s mechanistic insights.
marked upregulation in lipid metabolism, a
mechanism that not only promotes their proliferation but also manipulates stromal cells, like tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs),
contributing to an immuno suppressive tumor microenvironment (TME).
To interrogate the lipidomic environment of the TME, the researchers
utilized Cleanascite™ to selectively remove lipids and confirm the
lipid-dependence of TREM2+ TAM polarization. HCC-derived TIF potently
induced the expression of TREM2 and SPP1 in macrophages, which was
attributed to lipids…(Fig.). Consequently, Cleanascite™ enabled a
more precise functional dependency measurement, strengthening the
study’s mechanistic insights.