|
Cleanascite™ Employed to Determine Role of Lipids in Neutrophil Trafficking to Infection Sites Biotech Support Group reports on an article, describing their lipid clearance sample preparation technology to help determine the role of fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial metabolism in a cell response study of murine cell culture models of susceptib News Release
Cleanascite™ Employed to Determine Role of Lipids in Neutrophil Trafficking to Infection Sites
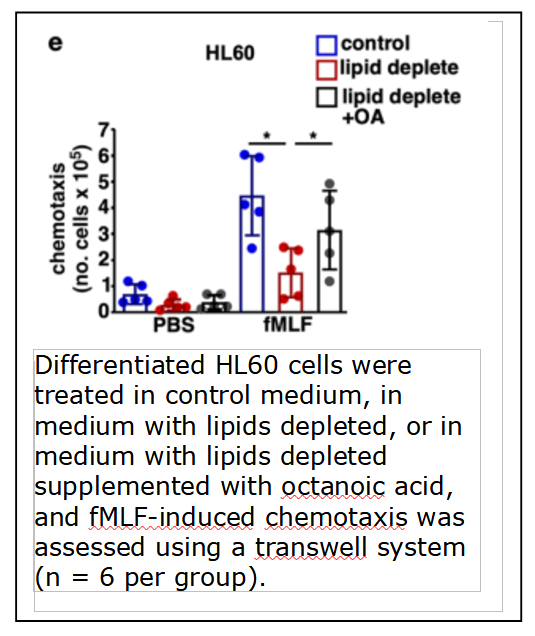
MONMOUTH JUNCTION, NJ, December 19, 2022 -- Biotech Support Group reports on an article, describing their lipid clearance sample preparation technology to help determine the role of fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial metabolism in a cell response study of murine cell culture models of susceptibility to infection. The citation is: Pham, Ly, et al. "Neutrophil trafficking to the site of infection requires Cpt1a-dependent fatty acid β-oxidation." Communications Biology 5.1 (2022): 1-13.
“We now have over twenty references, showing that Cleanascite™ was used to help identify a characteristic feature of in vitro cell response. Unlike alternative lipid-depletion methods that use solvents, Cleanascite™ is an aqueous suspension product and so it is very compatible with cellular models of disease. This ultimately helps with investigations such as this, whereby the cells require fetal bovine serum for growth, but the exogenous lipids need to be removed in order to determine their phenotypic effect.” states Swapan Roy, Ph.D., President and Founder of Biotech Support Group.
To download whitepaper entitled “Cleanascite™ - Lipid Removal and Cell Response Applications”, visit:
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a (Cpt1a), Neutrophil trafficking, Neutrophil chemotaxis, Cleanascite™, lipid depletion, mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation, microbial infection susceptibility
About Biotech Support Group LLC
Converging
with cultural and technological disruptions forthcoming in
healthcare, Biotech Support Group develops methods for cost effective
and efficient sample prep essential for these expanding markets.
Following a tiered business strategy, the company continues its
growth in the consumable research products area supporting the
rapidly expanding installation of LC-MS instrument and computational
infrastructure. For this market, key products include: AlbuVoid™
and AlbuSorb™ for albumin depletion, Cleanascite™ for lipid
adsorption, HemogloBind™ and HemoVoid™ for hemoglobin removal.
From these innovations, the company has acquired knowledgebase and
biomarker intellectual property assets that support discoveries of
protein markers from blood, with special emphasis on early detection
and personalized medical decisions for cancer patients. For more
information, go to http://www.biotechsupportgroup.com. For Business Development, contact: Matthew Kuruc 732-274-2866, mkuruc@biotechsupportgroup.com |

- About
- Products
- Hemoglobin Removal Kits
- Lipid Removal & Clarification
- Urine Protein & Low Abundance Enrichment
- Class Specific Enrichment
- Sample Prep Mass Spectrometry
- Functional & Chemical Proteomics
- Genomic Sample Prep
- Accessories
- Technical Resources
- References
- Publications & Reports
- FAQs
- Case Studies
- Cleanascite™ Unlocks Insights into Lipid-Driven Tumor Immunosuppression
- NRicher™ Bead Platform Provides Unique Sub-Proteome Biases And Fit For Purpose Opportunities for Targeted LC-MS Quantification
- BSG Products To Assist in Analyzing Macrophage Polarization
- Ectodomain Shedding and Enrichment of the Soluble Membrane Proteome
- Investigate out of the Venn Diagram box
- Methods to selectively deplete or purify Hemoglobin from Dried Blood Spots (DBS)
- The Utility of HemoVoid™ is Demonstrated in 3 Proteomic Investigations Identifying Potential Disease Specific Biomarkers
- The 4 common features of our sample prep products, known as the BSG Advantage, are highlighted in a selection of journal references.
- AlbuVoid™ Workflows Advance Cell Secretome Proteomics
- Lipid Removal for Phenotypic Cell Response in Cancer Research
- The Influence of Sample Prep Bias on LC-MS Targeted Peptide Quantification in Serum Proteomics
- Re-imagining proteomics for developing precision medicine biomarkers of the innate immune response in SARS-CoV-2
- Patent Application Describes New Proteomic Methods to Monitor Protease Inhibitor Function During Covid-19 Infections
- Efficient Hemoglobin Removal Advances Red Cell Proteomics Offering Many New Insights Into Inflammation and Infectious Disease
- The Potential for New Blood Biomarkers in the Management of COVID-19 Disease
- Establishing the Utility of HemoVoid™ and HemogloBind™ as Enrichment Tools for Proteomic Analysis of Red Cells and Whole Blood in Parkinson’s Disease
- Species Diversity Supported By BSG Products
- Poster Report Describes Loss of Functional Serpin Activity In Cancer Patient Blood
- AlbuVoid™️ PLUS & AlbuSorb™️ PLUS Evaluating Different Windows of Observation Solves The Many Challenges of Serum Proteomics
- Tackling the Challenges of Serum Proteomics
- Lipid Removal Sample Prep for Cell Response Applications
- Sample Prep for Proteomic Analysis of Saliva
- Biotech Support Group Featured in Book, "Functional Proteomics – Methods and Protocols"
- Sample Prep Liquid Biopsy Products Suitable for Proteomic Profiling of a Variety of Body Fluid Sample Types
- Albumin and High Abundance Depletion
- Using HemogloBind™ as a Hemoglobin Binding Reagent
- Diverse technologies available for researchers to selectively bind or enrich exosomes and extracellular vesicles.
- Stroma Liquid Biopsy™ Biomarkers Profile Pan-Cancer Dysregulation of the Serum Proteome
- Diverse Depletion and Enrichment Technologies Enhance Simplicity and Efficiency of Obtaining Quality Proteomic Information
- Use On-Bead Digestion to Improve Time Required for Serum Digestion
- Using AlbuVoid™ as a Serum Protein Enrichment Kit in Functional Proteomics
- Using Cleanascite™ as a Lipid Absorption and Clarification Reagent
- Using HemoVoid to Remove Hemoglobin Before Analysis
- Blog
- Contact
- Liquid Biopsy